Processing and adjustment of satellite geodetic networks
Showing all 3 results
Processing and adjustment of satellite geodetic networks involves the analysis and refinement of data collected from satellite-based positioning systems to establish precise geodetic networks. These networks are crucial for various applications such as surveying, mapping, geodesy, and geophysics. Here’s an overview of the process:
- Data Collection: Satellite geodetic networks typically utilize data from Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) such as GPS (Global Positioning System), GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System), Galileo, or BeiDou. Receivers on the ground collect observations of satellite signals, including pseudoranges, carrier phases, and satellite ephemeris data.
- Data Preprocessing: Raw GNSS data collected from multiple receivers are preprocessed to detect and remove errors and biases. This may include corrections for ionospheric and tropospheric delays, satellite clock errors, multipath effects, and receiver clock errors.
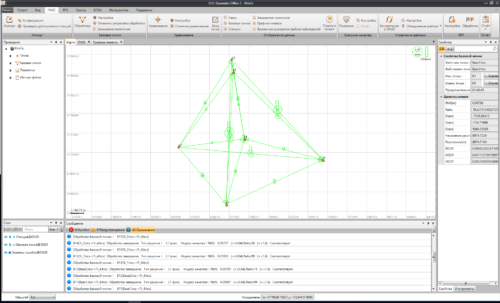
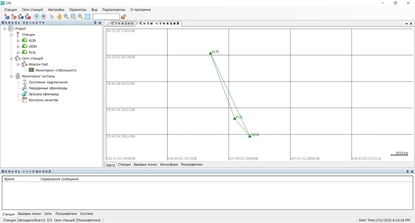
- Network Adjustment: The preprocessed data are then processed using geodetic network adjustment techniques to compute precise positions and velocities for the network’s control points (stations). The adjustment aims to minimize the discrepancies between observed and computed positions, taking into account the uncertainties and correlations in the observations.
- Least Squares Adjustment: The adjustment is typically performed using least squares estimation, which minimizes the sum of the squares of the residuals (the differences between observed and computed values). This iterative process iteratively refines the estimated parameters, including station coordinates, baseline vectors, and other relevant parameters.
- Modeling and Corrections: Various models and corrections are applied during the adjustment process to account for systematic errors and biases in the observations. This may include models for atmospheric effects, Earth’s gravity field, satellite orbit perturbations, and receiver and satellite antenna calibrations.
- Quality Control: After the adjustment, the quality of the computed network is assessed using statistical measures such as residuals analysis, covariance analysis, and outlier detection. This helps ensure the reliability and accuracy of the adjusted network.
- Datum Transformation: The adjusted network may need to be transformed to a specific geodetic datum or reference frame to align with other geodetic data sets or to meet project requirements.
- Reporting and Documentation: Finally, the results of the adjustment, including the computed coordinates and uncertainties for network stations, are documented in a report along with details of the adjustment methodology and any assumptions made.
Overall, processing and adjustment of satellite geodetic networks require expertise in geodesy, satellite positioning systems, and statistical estimation techniques. The resulting precise geodetic networks serve as a fundamental framework for various geospatial applications and scientific research.
Buy Processing and adjustment of satellite geodetic networks products in Uzbekistan, in Tashkent